Fuel pump capacity test. Fuel pressure leak down test
Before performing this test, verify fuel pump
pressure. Refer to Fuel Pump Pressure Test.
Use this test in conjunction with the Fuel Pressure
Leak Down Test.
(1) Release fuel system pressure. Refer to Fuel
Pressure Release Procedure.
(2) Disconnect fuel supply line at fuel rail. Refer to
Quick-Connect Fittings. Some engines may require
air cleaner housing removal before line disconnection.
(3) Obtain correct Fuel Line Pressure Test Adapter
Tool Hose. Tool number 6539 is used for 5/16" fuel
lines and tool number 6631 is used for 3/8" fuel lines.
(4) Connect correct Fuel Line Pressure Test
Adapter Tool Hose into disconnected fuel supply line.
Insert other end of Adaptor Tool Hose into a graduated
container.
(5) Remove fuel fill cap.
(6) To activate fuel pump and pressurize system,
obtain DRB scan tool and actuate ASD Fuel System
Test.
(7) A good fuel pump will deliver at least 1/4 liter
of fuel in 7 seconds. Do not operate fuel pump for
longer than 7 seconds with fuel line disconnected as
fuel pump module reservoir may run empty.
(a) If capacity is lower than specification, but
fuel pump can be heard operating through fuel fill
cap opening, check for a kinked/damaged fuel supply
line somewhere between fuel rail and fuel
pump module.
(b) If line is not kinked/damaged, and fuel pressure
is OK, but capacity is low, replace fuel filter/
fuel pressure regulator. The filter/regulator may be
serviced separately on certain applications. Refer
to Fuel Filter/Fuel Pressure Regulator Removal/Installation
for additional information.
(c) If both fuel pressure and capacity are low,
replace fuel pump module assembly. Refer to Fuel
Pump Module Removal/Installation. Use this test in conjunction with the Fuel Pump
Pressure Test and Fuel Pump Capacity Test.
Check Valve Operation: The electric fuel pump
outlet contains a one-way check valve to prevent fuel flow back into the
tank and to maintain fuel supply
line pressure (engine warm) when pump is not operational.
It is also used to keep the fuel supply line
full of gasoline when pump is not operational. After
the vehicle has cooled down, fuel pressure may drop
to 0 psi (cold fluid contracts), but liquid gasoline will
remain in fuel supply line between the check valve
and fuel injectors. Fuel pressure that has
dropped to 0 psi on a cooled down vehicle
(engine off) is a normal condition. When the electric
fuel pump is activated, fuel pressure should
immediately (1-2 seconds) rise to specification.
Abnormally long periods of cranking to restart a
hot engine that has been shut down for a short
period of time may be caused by: (1) Disconnect the fuel inlet line at fuel rail. Refer
to Fuel Tubes/Lines/Hoses and Clamps in this section
of the group for procedures. On some engines, air
cleaner housing removal may be necessary before
fuel line disconnection.
(2) Obtain correct Fuel Line Pressure Test Adapter
Tool Hose. Tool number 6539 is used for 5/16" fuel
lines and tool number 6631 is used for 3/8" fuel lines.
(3) Connect correct Fuel Line Pressure Test
Adapter Tool Hose between disconnected fuel line
and fuel rail (Fig. 8).
(4) Connect the 0-414 kPa (0-60 psi) fuel pressure
test gauge (from Gauge Set 5069) to the test port on
the appropriate Adaptor Tool. The DRB III Scan
Tool along with the PEP module, the 500 psi
pressure transducer, and the transducer-to-test
port adapter may also be used in place of the
fuel pressure gauge.
The fittings on both tools must be in good
condition and free from any small leaks before
performing the proceeding test. (5) Start engine and bring to normal operating
temperature.
(6) Observe test gauge. Normal operating pressure
should be 339 kPa 6 34 kPa (49.2 psi 6 5 psi).
(7) Shut engine off.
(8) Pressure should not fall below 30 psi for five
minutes.
(9) If pressure falls below 30 psi, it must be determined
if a fuel injector, the check valve within the
fuel pump module, or a fuel tube/line is leaking.
(10) Again, start engine and bring to normal operating
temperature.
(11) Shut engine off.
(12) Testing for fuel injector or fuel rail leakage:
Clamp off the rubber hose portion of Adaptor
Tool between the fuel rail and the test port "T" on
Adapter Tool. If pressure now holds at or above 30
psi, a fuel injector or the fuel rail is leaking.
(13) Testing for fuel pump check valve, filter/
regulator check valve or fuel tube/line leakage:
Clamp off the rubber hose portion of Adaptor Tool
between the vehicle fuel line and test port "T" on
Adapter Tool. If pressure now holds at or above 30
psi, a leak may be found at a fuel tube/line. If no
leaks are found at fuel tubes or lines, one of the
check valves in either the electric fuel pump or filter/
regulator may be leaking.
Note: A quick loss of pressure usually indicates a
defective check valve in the filter/regulator. A slow
loss of pressure usually indicates a defective check
valve in the electric fuel pump.
The electric fuel pump is not serviced separately.
Replace the fuel pump module assembly. The filter/
regulator may be replaced separately on certain
applications. Refer to Fuel Filter/Fuel Pressure Regulator
Removal/Installation for additional information.
1 - VEHICLE FUEL LINE 2 - TEST PORT "T" 3 - SPECIAL TOOL 6923, 6631, 6541 OR 6539 4 - FUEL PRESSURE TEST GAUGE 5 - FUEL LINE CONNECTION AT RAIL 6 - FUEL RAILFuel pump capacity test
Fuel pressure leak down test
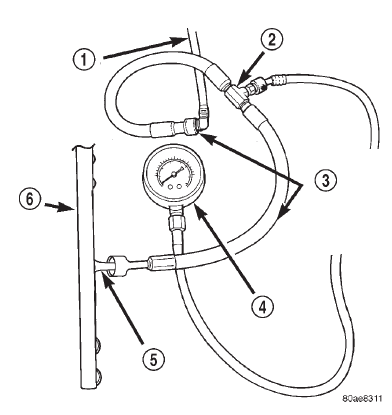 Fig. 8 Connecting Adapter Tool-Typical
Fig. 8 Connecting Adapter Tool-Typical
Dodge Durango (DN) 1998-2003 Service Manual
- Lubrication and Maintenance
- Suspension
- Differential and Driveline
- Brakes
- Cooling System
- Battery
- Starting Systems
- Charging System
- Ignition System
- Instrument Panel Systems
- Audio Systems
- Horn Systems
- Speed Control System
- Turn Signal and Hazard Warning Systems
- Wiper and Washer Systems
- Lamps
- Passive Restraint Systems
- Electrically Heated Systems
- Power Distribution System
- Power Lock Systems
- Vehicle Theft/Security Systems
- Power Seat System
- Power Window Systems
- Power Mirror Systems
- Chime/Buzzer Warning Systems
- Overhead Console Systems
- Engine
- Exhaust System
- Frame and Bumpers
- Fuel System
- Steering
- Transmission and Transfer Case
- Tires and Wheels
- Body
- Heating and Air Conditioning
- Emission Control Systems
- Introduction
