Visual inspection-3.9/5.2/5.9L engines
A visual inspection for loose, disconnected or incorrectly routed wires and hoses should be made. This should be done before attempting to diagnose or service the fuel injection system. A visual check will help spot these faults and save unnecessary test and diagnostic time. A thorough visual inspection will include the following checks: (1) Verify three 32-way electrical connectors are fully inserted into connector of powertrain control module (PCM) (Fig. 3).
(2) Inspect battery cable connections. Be sure they are clean and tight.
(3) Inspect fuel pump relay and air conditioning compressor clutch relay (if equipped). Inspect ASD relay connections. Inspect starter motor relay connections.
Inspect relays for signs of physical damage and corrosion. The relays are located in Power Distributiontion Center (PDC) (Fig. 4). Refer to label on PDC cover for relay location.
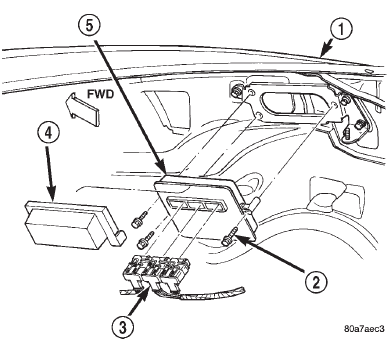 Fig. 3 Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
Fig. 3 Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
1 - RIGHT FRONT FENDER
2 - PCM MOUNTING BOLTS (3)
3 - 32-WAY CONNECTORS (3)
4 - COVER
5 - POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (PCM)
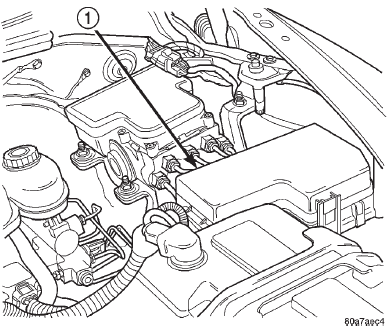 Fig. 4 Power Distribution Center (PDC)
Fig. 4 Power Distribution Center (PDC)
1 - POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER (PDC)
(4) Inspect ignition coil connections. Verify coil secondary cable is firmly connected to coil (Fig. 5).
(5) Verify distributor cap is correctly attached to distributor. Be sure spark plug cables are firmly connected to the distributor cap and the spark plugs are in their correct firing order. Be sure coil cable is firmly connected to distributor cap and coil. Be sure camshaft position sensor wire connector (at the distributor) is firmly connected to harness connector.
Inspect spark plug condition. Refer to Group 8D, Ignition. Connect vehicle to an oscilloscope and inspect spark events for fouled or damaged spark plugs or cables.
(6) Verify generator output wire, generator connector and ground wire are firmly connected to generator.
(7) Inspect system body grounds for loose or dirty connections. Refer to Group 8, Wiring for ground locations.
(8) Verify positive crankcase ventilation (PCV) valve operation. Refer to Group 25, Emission Control System for additional information. Verify PCV valve hose is firmly connected to PCV valve and manifold (Fig. 6).
(9) Inspect fuel tube quick-connect fitting-to-fuel rail connections.
(10) Verify hose connections to all ports of vacuum fittings on intake manifold are tight and not leaking.
(11) Inspect accelerator cable, transmission throttle cable (if equipped) and cruise control cable connections (if equipped). Check their connections to throttle arm of throttle body for any binding or restrictions.
(12) If equipped with vacuum brake booster, verify vacuum booster hose is firmly connected to fitting on intake manifold. Also check connection to brake vacuum booster.
(13) Inspect air cleaner inlet and air cleaner element for dirt or restrictions.
(14) Inspect radiator grille area, radiator fins and air conditioning condenser for restrictions.
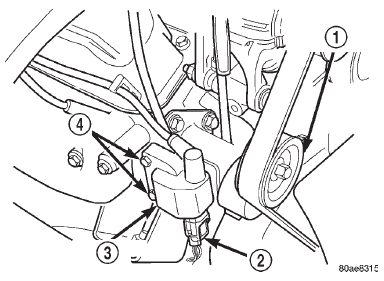 Fig. 5 Ignition Coil
Fig. 5 Ignition Coil
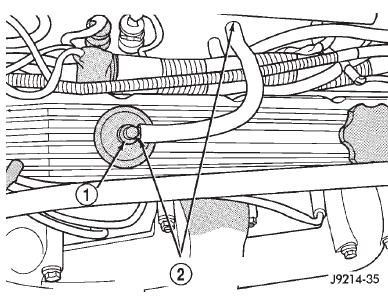 Fig. 6 PCV Valve Hose Connections
Fig. 6 PCV Valve Hose Connections
1 - PCV VALVE
2 - PCV VALVE HOSE CONNECTIONS
(15) Verify intake manifold air temperature sensor wire connector is firmly connected to harness connector (Fig. 7).
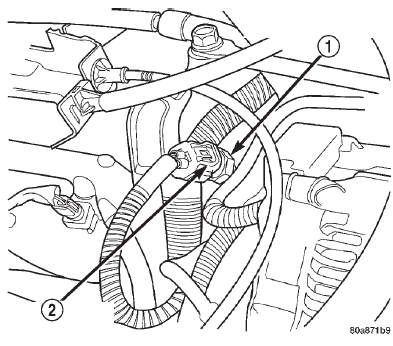 Fig. 7 Intake Manifold Air Temperature Sensor- Typical
Fig. 7 Intake Manifold Air Temperature Sensor- Typical
1 - INTAKE MANIFOLD AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR
2 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
(16) Verify MAP sensor electrical connector is firmly connected to MAP sensor (Fig. 8). Also verify rubber L-shaped fitting from MAP sensor to throttle body is firmly connected (Fig. 9).
(17) Verify fuel injector wire harness connectors are firmly connected to injectors in correct order.
Each harness connector is numerically tagged with injector number (INJ 1, INJ 2 etc.) of its corresponding fuel injector and cylinder number.
(18) Verify harness connectors are firmly connected to idle air control (IAC) motor, throttle position sensor (TPS) and manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor (Fig. 8).
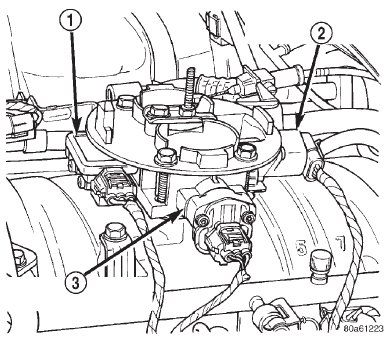 Fig. 8 Sensor and IAC Motor Location-Typical (V-8 Shown)
Fig. 8 Sensor and IAC Motor Location-Typical (V-8 Shown)
1 - MAP SENSOR
2 - IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR
3 - THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
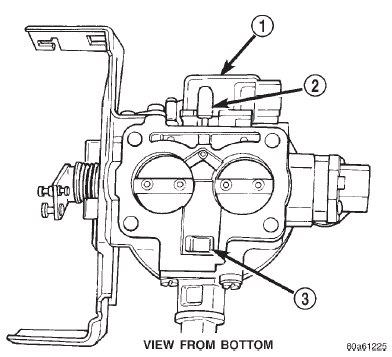 Fig. 9 Rubber L-Shaped Fitting-MAP Sensor-to- Throttle Body
Fig. 9 Rubber L-Shaped Fitting-MAP Sensor-to- Throttle Body
1 - MAP SENSOR
2 - RUBBER FITTING
3 - IDLE AIR PASSAGE
(19) Verify wire harness connector is firmly connected to engine coolant temperature sensor (Fig.
10).
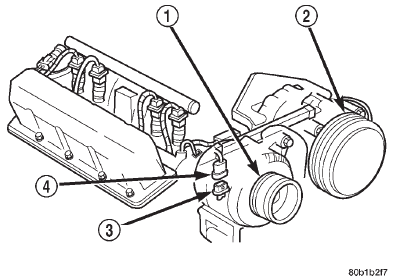 Fig. 10 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
Fig. 10 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
1 - GENERATOR
2 - A/C COMPRESSOR
3 - ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
4 - ELEC. CONN.
(20) Raise and support vehicle.
(21) Verify both upstream and downstream oxygen sensor wire connectors are firmly connected to sensors.
Inspect sensors and connectors for damage (Fig.
11) or (Fig. 12).
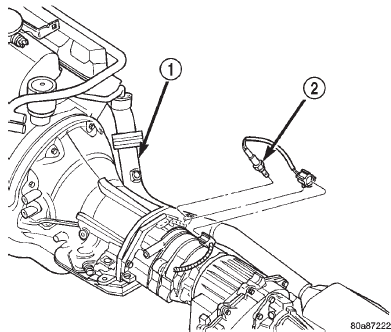 Fig. 11 Upstream Oxygen Sensor
Fig. 11 Upstream Oxygen Sensor
1 - EXHAUST PIPE
2 - UPSTREAM OXYGEN SENSOR
(22) Inspect for pinched or leaking fuel tubes.
Inspect for pinched, cracked or leaking fuel hoses.
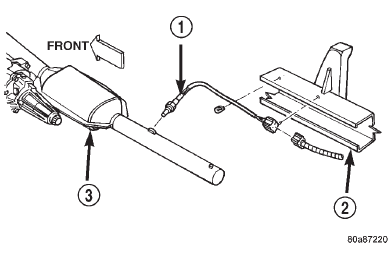 Fig. 12 Downstream Oxygen Sensor
Fig. 12 Downstream Oxygen Sensor
1 - DOWNSTREAM OXYGEN SENSOR
2 - FRAME RAIL
3 - CATALYTIC CONVERTER
(23) Inspect for exhaust system restrictions such as pinched exhaust pipes, collapsed muffler or plugged catalytic convertor.
(24) If equipped with automatic transmission, verify electrical harness is firmly connected to park/neutral switch. Refer to Automatic Transmission section of Group 21.
(25) Verify electrical harness is firmly connected to rear wheel speed sensor. Verify rear wheel speed sensor is firmly attached to rear axle with proper air gap. Refer to Group 5, Brakes for information.
(26) If equipped with 4-wheel antilock brake system, verify electrical harness is firmly connected to each front wheel speed sensor. Verify both front wheel speed sensors are firmly attached. Refer to Group 5, Brakes for information.
(27) Verify fuel pump/gauge sender unit wire connector is firmly connected to harness connector.
(28) Inspect fuel hoses at fuel pump/gauge sender unit for cracks or leaks.
(29) Inspect transmission torque convertor housing (automatic transmission) or clutch housing (manual transmission) for damage to timing ring on drive plate/flywheel.
(30) Verify battery cable and solenoid feed wire connections to starter solenoid are tight and clean.
Inspect for chaffed wires or wires rubbing against other components.
Dodge Durango (DN) 1998-2003 Service Manual
- Lubrication and Maintenance
- Suspension
- Differential and Driveline
- Brakes
- Cooling System
- Battery
- Starting Systems
- Charging System
- Ignition System
- Instrument Panel Systems
- Audio Systems
- Horn Systems
- Speed Control System
- Turn Signal and Hazard Warning Systems
- Wiper and Washer Systems
- Lamps
- Passive Restraint Systems
- Electrically Heated Systems
- Power Distribution System
- Power Lock Systems
- Vehicle Theft/Security Systems
- Power Seat System
- Power Window Systems
- Power Mirror Systems
- Chime/Buzzer Warning Systems
- Overhead Console Systems
- Engine
- Exhaust System
- Frame and Bumpers
- Fuel System
- Steering
- Transmission and Transfer Case
- Tires and Wheels
- Body
- Heating and Air Conditioning
- Emission Control Systems
- Introduction
