Evaporation (evap) canister. Duty cycle evap canister purge solenoid
DESCRIPTION A maintenance free, EVAP canister is used on all
vehicles. The EVAP canister is located under the
vehicle, inside the left frame rail, in front of the fuel
tank (Fig. 2).
1 - LEFT FRAME RAIL 2 - RUBBER GROMMETS (2) 3 - LOCATING PINS (2) 4 - EVAP CANISTER 5 - MOUNTING NUT 6 - MOUNTING BRACKET OPERATION The EVAP canister is filled with granules of an
activated carbon mixture. Fuel vapors entering the
EVAP canister are absorbed by the charcoal granules.
Fuel tank pressure vents into the EVAP canister.
Fuel vapors are temporarily held in the canister until
they can be drawn into the intake manifold. The duty
cycle EVAP canister purge solenoid allows the EVAP
canister to be purged at predetermined times and at
certain engine operating conditions. OPERATION The duty cycle EVAP canister purge solenoid (DCP)
regulates the rate of vapor flow from the EVAP canister
to the intake manifold. The Powertrain Control
Module (PCM) operates the solenoid. During the cold start warm-up period and the hot
start time delay, the PCM does not energize the solenoid.
When de-energized, no vapors are purged. The
PCM de-energizes the solenoid during open loop operation.
The engine enters closed loop operation after it
reaches a specified temperature and the time delay
ends. During closed loop operation, the PCM cycles
(energizes and de-energizes) the solenoid 5 or 10
times per second, depending upon operating conditions.
The PCM varies the vapor flow rate by changing
solenoid pulse width. Pulse width is the amount
of time that the solenoid is energized. The PCM
adjusts solenoid pulse width based on engine operating
condition.Evaporation (evap) canister
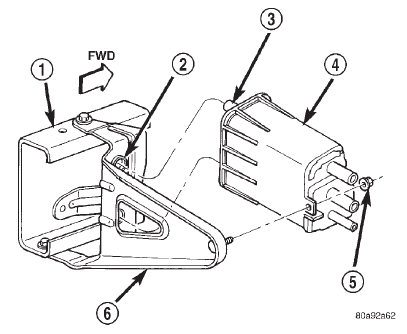 Fig. 2 EVAP Canister Location
Fig. 2 EVAP Canister LocationDuty cycle evap canister purge solenoid
Dodge Durango (DN) 1998-2003 Service Manual
- Lubrication and Maintenance
- Suspension
- Differential and Driveline
- Brakes
- Cooling System
- Battery
- Starting Systems
- Charging System
- Ignition System
- Instrument Panel Systems
- Audio Systems
- Horn Systems
- Speed Control System
- Turn Signal and Hazard Warning Systems
- Wiper and Washer Systems
- Lamps
- Passive Restraint Systems
- Electrically Heated Systems
- Power Distribution System
- Power Lock Systems
- Vehicle Theft/Security Systems
- Power Seat System
- Power Window Systems
- Power Mirror Systems
- Chime/Buzzer Warning Systems
- Overhead Console Systems
- Engine
- Exhaust System
- Frame and Bumpers
- Fuel System
- Steering
- Transmission and Transfer Case
- Tires and Wheels
- Body
- Heating and Air Conditioning
- Emission Control Systems
- Introduction
