Description and operation. Diagnosis and testing
WHEEL ALIGNMENT DESCRIPTION Wheel alignment involves the correct positioning of
the wheels in relation to the vehicle. The positioning
is accomplished through suspension and steering
linkage adjustments. An alignment is considered
essential for efficient steering, good directional stability
and to minimize tire wear. The most important
measurements of an alignment are caster, camber
and toe (Fig. 1). CAUTION: Never attempt to modify suspension or
steering components by heating or bending. NOTE: Periodic lubrication of the front suspension/
steering system components may be required. Rubber
bushings must never be lubricated. Refer to
Group 0, Lubrication And Maintenance for the recommended
maintenance schedule. OPERATIONDescription and operation
Positive caster promotes directional stability. This angle enables the front wheels to return to a straight ahead position after turns.
Tilting the top of the wheel outward provides positive camber. Incorrect camber will cause wear on the inside or outside edge of the tire.
Diagnosis and testing
PRE-ALIGNMENT INSPECTION
Before starting wheel alignment, the following inspection and necessary corrections must be completed.
Refer to Suspension and Steering System Diagnosis Chart for additional information.
(1) Inspect tires for size, air pressure and tread wear.
(2) Inspect front wheel bearings for wear.
(3) Inspect front wheels for excessive radial or lateral runout and balance.
(4) Inspect ball studs, linkage pivot points and steering gear for looseness, roughness or binding.
(5) Inspect suspension components for wear and noise.
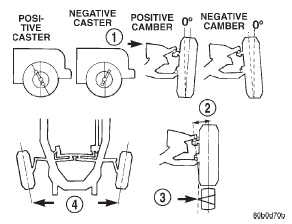 Fig. 1 Wheel Alignment Measurements
Fig. 1 Wheel Alignment Measurements
SUSPENSION AND STEERING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
| CONDITION | POSSIBLE CAUSES | CORRECTION |
| FRONT END NOISE | 1. Loose or worn wheel bearing. 2. Loose or worn steering or suspension components. 3. Lower ball joint (4x4). |
1. Replace wheel bearing. 2. Tighten or replace components as necessary. 3. Gease joint and perform diagnosis and testing. |
| EXCESSIVE PLAY IN STEERING | 1. Loose or worn wheel bearing. 2. Loose or worn steering or suspension components. 3. Loose or worn steering gear. |
1. Replace wheel bearing. 2. Tighten or replace components as necessary. 3. Adjust or replace steering gear. |
| FRONT WHEELS SHIMMY | 1. Loose or worn wheel bearing. 2. Loose or worn steering or suspension components. 3. Tires worn or out of balance. 4. Alignment. |
1. Replace wheel bearing. 2. Tighten or replace components as necessary. 3. Replace or balance tires. 4. Align vehicle to specifications. |
| VEHICLE INSTABILITY | 1. Loose or worn wheel bearing. 2. Loose or worn steering or suspension components. 3. Tire pressure. 4. Alignment. |
1. Replace wheel bearing. 2. Tighten or replace components as necessary. 3. Adjust tire pressure. 4. Align vehicle to specifications. |
| EXCESSIVE STEERING EFFORT | 1. Loose or worn steering gear. 2. Column coupler binding. 3. Tire pressure. 4. Alignment. |
1. Adjust or replace steering gear. 2. Replace coupler. 3. Adjust tire pressure. 4. Align vehicle to specifications. |
| VEHICLE PULLS TO ONE SIDE | 1. Tire pressure. 2. Alignment. 3. Loose or worn steering or suspension components. 4. Radial tire lead. 5. Brake pull. 6. Weak or broken spring. 7. Ride height 4WD only. |
1. Adjust tire pressure. 2. Align vehicle to specifications. 3. Tighten or replace components as necessary. 4. Rotate or replace tire as necessary 5. Repair brake as necessary. 6. Replace spring. 7. Measure and adjust ride height. |
Dodge Durango (DN) 1998-2003 Service Manual
- Lubrication and Maintenance
- Suspension
- Differential and Driveline
- Brakes
- Cooling System
- Battery
- Starting Systems
- Charging System
- Ignition System
- Instrument Panel Systems
- Audio Systems
- Horn Systems
- Speed Control System
- Turn Signal and Hazard Warning Systems
- Wiper and Washer Systems
- Lamps
- Passive Restraint Systems
- Electrically Heated Systems
- Power Distribution System
- Power Lock Systems
- Vehicle Theft/Security Systems
- Power Seat System
- Power Window Systems
- Power Mirror Systems
- Chime/Buzzer Warning Systems
- Overhead Console Systems
- Engine
- Exhaust System
- Frame and Bumpers
- Fuel System
- Steering
- Transmission and Transfer Case
- Tires and Wheels
- Body
- Heating and Air Conditioning
- Emission Control Systems
- Introduction
